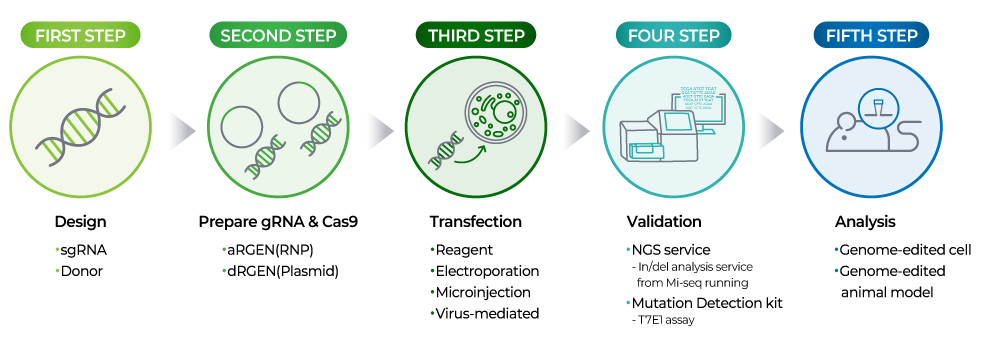
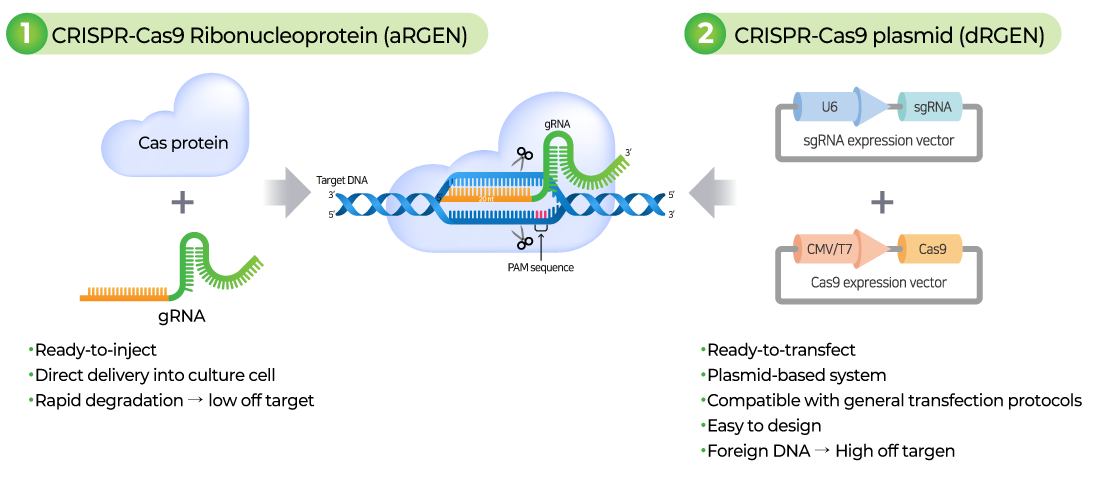
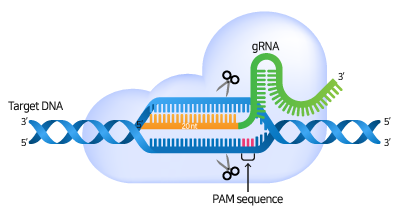
CRISPR Cas9 technology is an innovative gene editing technology that allows precise modification of the DNA of living organisms. It consists of a guide RNA (gRNA) that accurately recognizes and binds to the target DNA and a Cas9 nuclease that cuts the target DNA, allowing genes to be manipulated through the process of damaging and repairing DNA double strands.
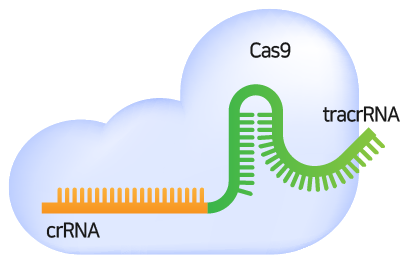
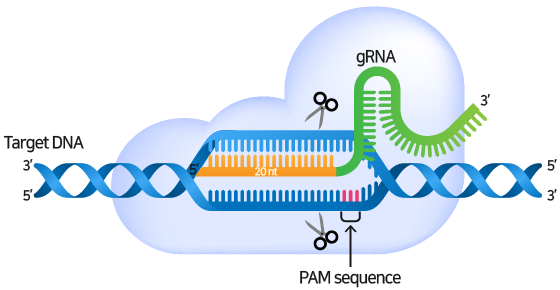
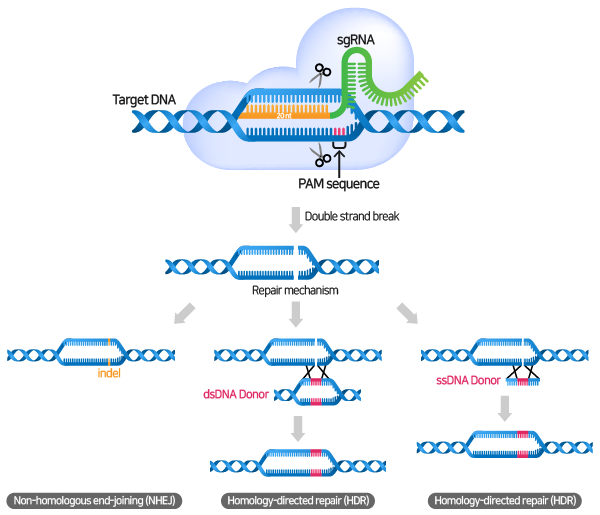
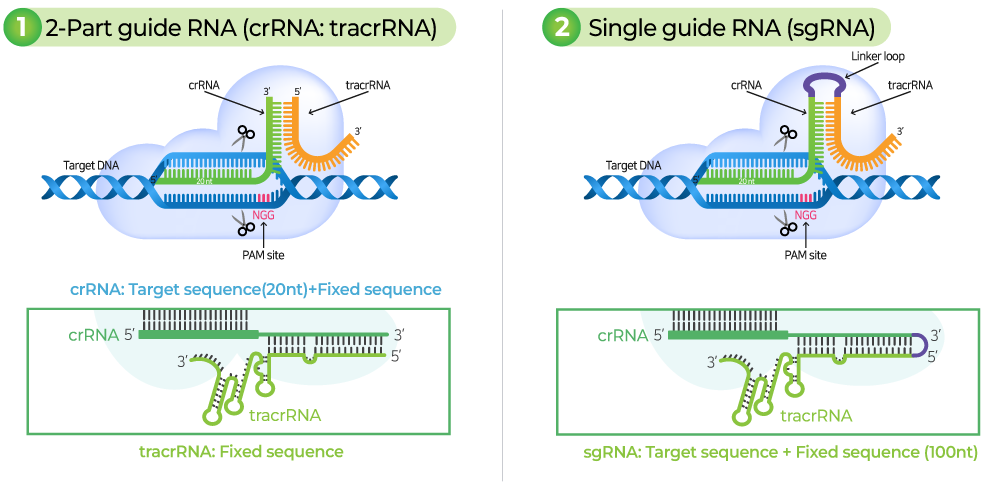
gRNA consists of crRNA that binds complementary to the target sequence and tracrRNA for Cas9-binding. gRNA serves to guide Cas9 to the target region and binds complementary to the target DNA sequence. There must be a PAM (Protospacer adjacent motif) sequence at the 3' end of the target DNA sequence.
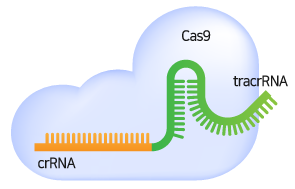
When the gRNA forms a complex with the Cas9 nuclease and specifically binds to the target sequence, the Cas9 nuclease recognizes the PAM sequence and causes a double strand break (DSB) in the 3 bp upstream part of the PAM.
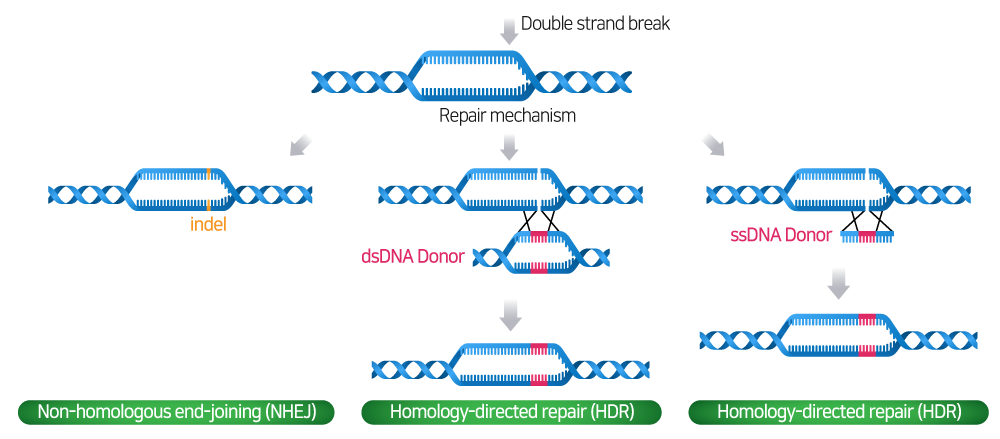
To repair DNA damaged by DSBs, cells generally go through two pathways: Non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) or Homology-directed repair (HDR) pathway.
- NHEJ pathway: In the absence of a donor template, DSBs are reassembled through the NHEJ pathway, and gene knock-outs are created due to frameshifts and premature stop codons caused by the creation of indels (insertions and deletions) within the gene coding region.
- HDR pathway: The HDR pathway allows precise and accurate modifications and insertion of new genes by donor templates.