We use cookies to give you the best online experience. By using our website you agree to our use of cookies in accordance with our Cookie Policy
S. pombe Genome-wide Heterozygous Deletion Mutant Screening Service

BIONEER's unique Drug Target & Toxicity Identification Services: GPScreen™-FAST
An Innovative Technology for Drug Target Identification using Drug-induced Haploinsufficiency (DIH) in the World's First Fission Yeast S. pombe Genome-wide Heterozygous Deletion Mutant Library
Features and Benefits of GPScreen™-FAST
-
The world's only innovative drug target identification technology based on S. pombe Genome-wide Deletion Mutant Library
-
Almost all types of drug targets possible to be screened at the genome level
-
Live cell-based screening
-
Fast and accurate screening service through barcode NGS
-
Applicable to drug repositioning, natural drug target discovery, drug toxicity evaluation
GPScreen™-FAST Application
-
Drug target Identification and drug toxicity evaluation
-
Drug prioritization
-
Drug repositioning and drug efficacy improvement
-
Natural drug target discovery and mechanism of action (MOA) study
-
Chemogenomic profiling
Overview
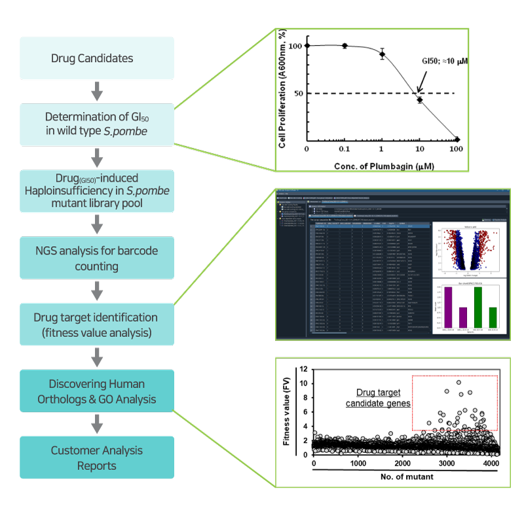
Accurate drug target identification is the first and the most crucial step for not only increasing the success rate for the new drug development, but also understanding the mode-of-actions, improving efficacy, tracing and avoiding side-effects. Bioneer has developed a new a high-throughput genome-wide drug target screening system called GPScreen™-FAST and made it commercially available for researchers to be used for their drug discovery needs. This technology covers a broad spectrum of drug candidates in most of disease areas from cancers & metabolic diseases to neglected & rare diseases. This will ultimately provide the total solutions for an efficient drug discovery through providing clear-cut answers to problems such as drug-target(s) and toxicity as well as mode-of-actions of drug candidates.
GPScreen™-FAST is based on S. pombe genome-wide deletion mutant library, developed together with Bioneer and the Korea Research Institute of Bioscience & Biotechnology (KRIBB) in collaboration with Dr. Paul Nurse of Cancer Research Center UK (Nat. Biotech, 28, 617–623, 2010). However, Bioneer has all the business' exclusive rights to this library and provides it for genetic and chemical screening such as drug target identification, gene expression profiling and synthetic lethal profiling.
The genomic library covers about 98.5% of the entire genome of the fission yeast S. pombe. Individual variants are those in which one of the pairs of individual genes in normal cells is deficient due to the insertion of a DNA barcode cassette through homologous recombination (Refer to image). We pool all the strains that are balanced-grown and calculate their DNA barcode using NGS analysis.
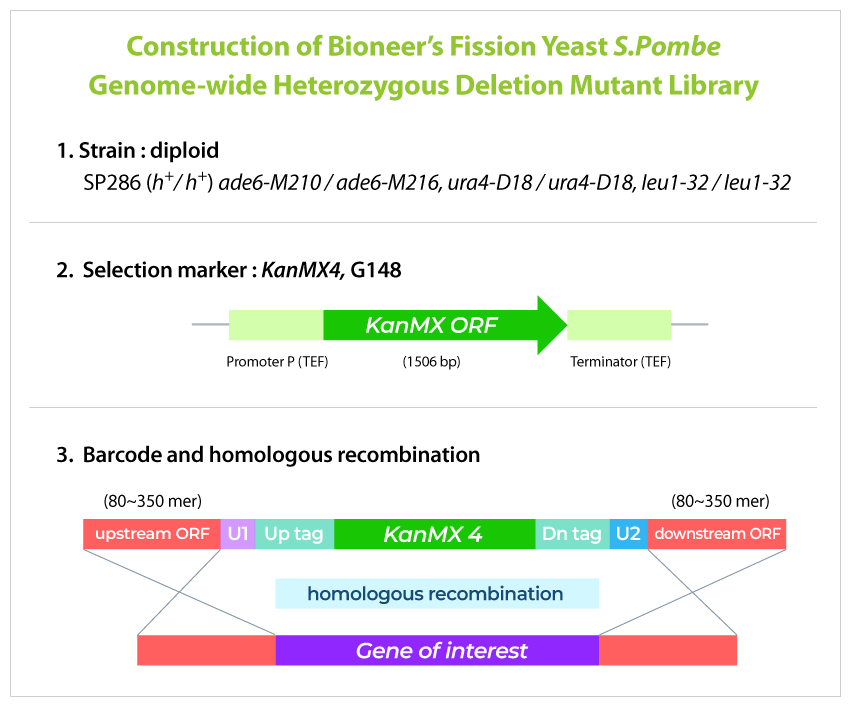
GPScreen™-FAST Principle
'Drug-induced Haploinsufficiency (DIH)' refers to the increased sensitivity of a heterozygous deletion mutant (a variant in which a specific protein is expressed to about half of a normal level) to a specific drug. This phenomenon occurs when a drug acts on a mutant in which a particular gene is missing, therefore, it is regarded as a useful assay strategy for drug target identification. Previously, a number of reports have provided identifications of drug targets using DIH in the budding yeast S. cerevisiae (Baetz K et al., 2004; Lum et al., 2004). However, the fission yeast S.pombe is considered more ideal model yeast than S.cerevisiae since it share more physiological process with mammalian cell than S.cerevisiae (Vyas A et al., 2021).
In the GPScreen™-FAST service, to confirm drug sensitivity of individual mutant strains, distinct DNA barcode count of all strains is calculated through NGS. Furthermore, the fitness value (FV) of each gene is analyzed quickly and accurately from the obtained NGS data using GPScreen Analysis Software (GPSAS), ultimately suggesting potential drug target genes.
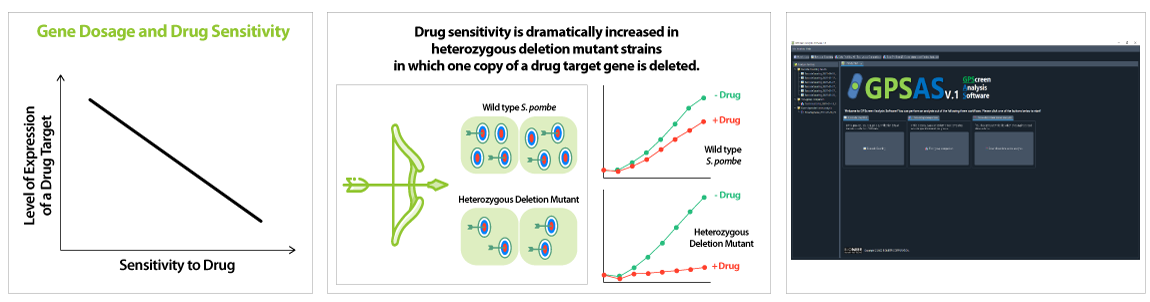
GPScreen™-FAST Performance
GPScreen™-FAST technology can accurately define the drug targets at the genome level.
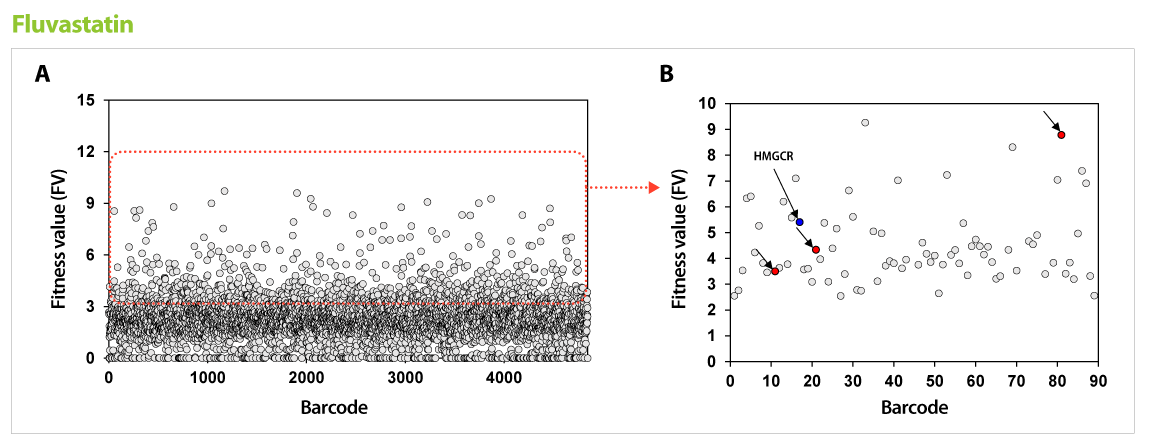
Figure 1. Results of GPScreen™-FAST to discover candidate target genes of Fluvastatin. (A) Barcode counts by NGS analysis. Barcode number of total mutant strains (pool) was read by NGS analysis. (B) Candidate target genes of Fluvastatin. Among selected candidate genes from GPScreenTM-FAST (red boundary in (A)), drug-induced haploinsufficiency (DIH) assay in individual mutant strain was performed as a secondary screening. As a results, known-target gene (HMGCR, blue circle) and expected-target genes (red circle) were detected.
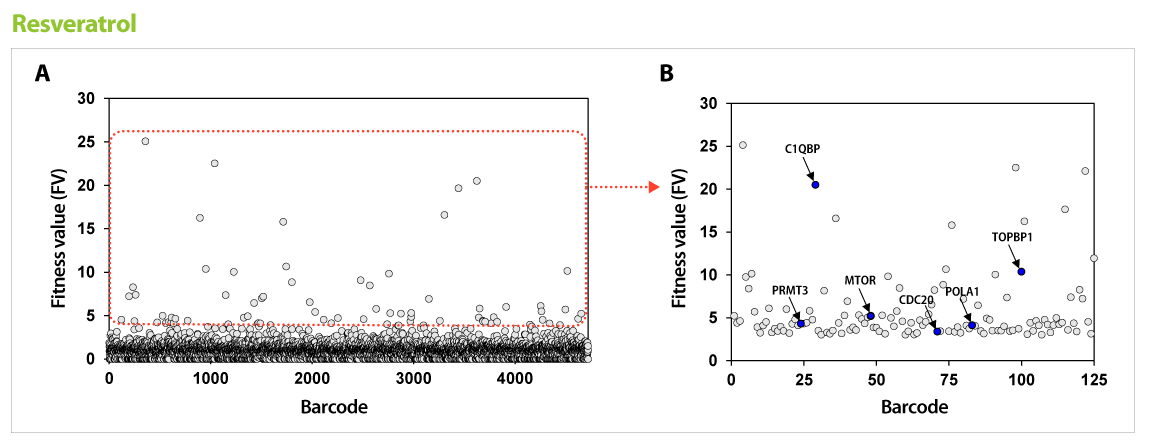
Figure 2. Results of GPScreen™-FAST to discover candidate target genes of Resveratrol. (A) Barcode counts by NGS analysis. Barcode number of total mutant strains (pool) was read by NGS analysis. (B) Candidate target genes of Resveratrol. Among selected candidate genes from GPScreenTM-FAST (red boundary in (A)), drug-induced haploinsufficiency (DIH) assay in individual mutant strain was performed as a secondary screening. As a results, known-target genes (blue circle) were discovered.


▶ Using the drug action point discovered via GPScreen™ , target validation studies are possible on human cells.
IMethods for Validating Drug Targets in Human Cells
Bioneer has about 20,000 siRNA libraries for human genes.
By using the human orthologs of the identified target candidates from GPScreen™, gene knockdown can be analyzed to verify the gene in human cells using the siRNA library.
1) Analysis of human homologous gene expression regulation by drugs in human cells
Figure 1. Photos and the graphs showing the inhibition of POLG expression by Sunitinib in the Hela human cell lines
(A) To measure the cellular responses of Hela cells to sunitinib, the cells were spread onto m-slide 8-well plates and treated with 0 µM or 5 µM of sunitinib for 48 h. Then, the level of POLG proteins was observed with immunocytochemistry using an anti-POLG antibody and goat anti-rabbit IgG-TRITC antibody in fluorescent confocal microscope.
(B) Hela cells were treated with 0 µM or 5 µM of sunitinib for 48 h, and POLG mRNA levels in the treated cells were measured by qRT-PCR.
2) Analysis of inhibitory effect of human homologous gene expression using BIoneer's human siRNA library
Figure 2. Photos and the graphs showing the knockdown of POLG dramatically increased the cytotoxicity by sunitinib in a human cell line (Hela cells).
(Upper panel) After the treatment of siRNAs (5 nM, 48 h), the cells were further treated with sunitinib (5 µM) for 48 h, and the cell mass was measured by SRB assay.
(Bottom panel) The cells that have went through SRB assay were observed under a microscope.
IIApplication of GPScreen™ technology to derive new drug development candidates
In addition, GPScreen™ technology is also available for the screening of safer compounds between drug candidates in the early stages of new drug development for comparison. When this technology was used for analysis of target profiles at the genome level, toxic drugs showed a broader target spectrum than non-toxic drugs. It represents the toxicity profile of the drug in the human body and can be used effectively for drug prioritization for the safest drug among the same kind of candidate substances.
Figure 3. Targeted spectrum comparison after GPScreen™ each toxic and nontoxic drugs